Wednesday, 19 March 2014
Bearings and loci
Objectives
Bearings
Locus from a fixed point
Constructing a perpendicular bisector
(to find the locus that is equidistant from two points)
Locus from a line
Constructing the bisector of an angle
(to find the locus that is equidistant from two lines)
Bearings
Locus from a fixed point
A locus means a path. 'Loci' is the plural of locus. It shows us the path or region that a point can travel according to certain rules.
The locus of points that are equidistant from two points: Constructing a Perpendicular Bisector
You can find the method by clicking on the image below:Watch the video.
The locus of all points that are equidistant from two lines: Bisecting an angle
We use this method to find the locus of all points that are equidistant from two lines.
Some real world examples of loci
Watch a video of how loci apply in the real world.
Labels:
Grade 8 Maths
Tuesday, 18 March 2014
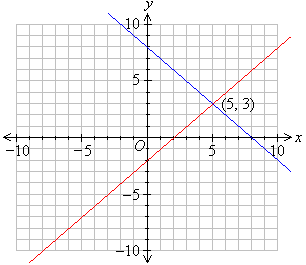
Graphing and Solving Linear Equations
- The equation of a line
- Solving two simultaneous equations using a graph
- Trial and Improvement method to solve an equation
Linear Equations
Solving two simultaneous equations using a graph
Trial and Improvement method to solve an equation
Using this method we 'guess' the first value x and then try other values until we find one that works. Click the image below for an example:
Labels:
Grade 8 Maths
Monday, 10 March 2014
Tuesday, 4 February 2014
Constructions
- Constructing the perpendicular bisector of a line
- Finding the perpendicular from a point to a line
- Bisecting an angle
Watch the video.
- Finding the perpendicular from a point to a line
- Bisecting an angle
Constructing a Perpendicular Bisector
You can find the method by clicking on the image below:Watch the video.
Bisecting an angle
Labels:
Grade 8 Maths
Sunday, 2 February 2014
Angles of Polygons
Interior and Exterior Angles
Exterior Angles of a Polygon
Remember, a polygon is any shape that has 3 or more straight sides (no curves).
Click on the hexagon above to see that:
The exterior angles of any polygon add up to 360°
Interior Angles
 |  |
90° + 60° + 30° = 180° | 80° + 70° + 30° = 180° |
It works for this triangle!
|
Let's tilt a line by 10° ...
It still works, because one angle went up by 10°, but the other went down by 10°
|
The Interior Angles of a Triangle add up to 180°
| The interior angles in this triangle add up to 180° (90°+45°+45°=180°) |  | ... and for this square they add up to 360° ... because the square can be made from two triangles! |
Because a pentagon has three triangles, the sum of the interior angles add up to 3x180° = 540°
In general:
The sum of the interior angles of a polygon that has n sides, is:
(n-2) x 180°
Triangles in a circle:
The triangle drawn on the diameter of a circle is always
a right angled triangle
Labels:
Grade 8 Maths
Monday, 13 January 2014
Areas and volumes
Objectives:
Area of rectangles and triangles
Area of parallelograms and trapeziums
Volume of cuboids
Parts of a circle, circumference and area.
Area of a rectangle:
Area of a triangle:
More: Area of a triangle inside a rectangleArea of a parallelogram:
Area of a trapezium:
(Note: this shape is also known as a trapezoid, but for your exam just use trapezium!)Cuboids
A cuboid is a box-shaped object. Click the image below for more information.
V = l × w × h
Nets
A 'net' is the shape you get when you cut along the edges of a three dimensional object and lay it out flat.Parts of a circle:
Copy the picture below, label the green and blue sections:
Answer is here.
>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>
Circle: Area and circumference
Homework:
P162 Ex 18.1 Q 3
P165 Ex 18.2A Q3
P165 Ex 18.2B Q 1b, Q2b
P170 Ex 18.3B Q 1, 2
P172 Ex 18.4 Q 3
P174 Ex 18.5A Q 1 - 9
P176 Ex 18.5B Q 1c, 1d, 2c, 2d.
P177 Ex 18.5C d, e
Labels:
Grade 8 Maths
Saturday, 11 January 2014
Similar Triangles and Sine, Cosine, Tangent.
-
Identify similar shapes
Use Sin, Cos and Tan for acute angles
Similarity
Two shapes are Similar if the only difference is size (and possibly the need to turn or flip one around). Information on similar triangles.See if you can figure out how tall a tree is without having to measure its height:
Right angled triangle ratios
Sine, Cosine and Tangent ratios
Remember:Sohcahtoa
Soh...
|
Sine = Opposite / Hypotenuse
|
...cah...
|
Cosine = Adjacent / Hypotenuse
|
...toa
|
Tangent = Opposite / Adjacent
|
Click the image below for some extra exercises and further information:
Homework:
P289 Ex1 Q. 6, 11, 13, 16, 17
P293 Ex 2 Q. 17-20
P293 Ex 3 Q. 4, 6, 7, 10, 11, 12
Labels:
Grade 9 Maths
Tuesday, 7 January 2014
Angle Properties
Identify: Supplementary, vertically opposite, corresponding and alternate angles.
Know that angles of a triangle add up to 180°
Know that the exterior angle of triangle is equal to the sum of the two interior opposite angles.
Know that angles of a quadrilateral add up to 360°
Supplementary Angles (add to 180°)
Vertically Opposite Angles..... are equal
Corresponding Angles (look for an 'F' shape)...... are equal
Alternate Angles (look for a 'Z' shape)....are equal
Angles of a triangle add up to 180°
A + B + C = 180°
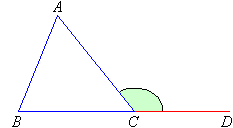
Exterior angle of triangle is equal to the sum of the two interior opposite angles.
C = A + B
Angles of a quadrilateral add up to 360°
80° + 100° + 90° + 90° = 360°
Homework:
P153 Ex 16.4C Q3-6
P156 Ex 17.1B Q4-8
P158 Ex 17.2 Q3, 5, 6
P160 Ex 17.3A Q3, 4
P160 Ex 17.3B Q1, 4
Labels:
Grade 8 Maths
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)